Nursing is a noble profession, offering diverse opportunities in healthcare systems worldwide. Among the top countries for pursuing a nursing career are India and the United States. While both countries provide rewarding careers, their approaches, opportunities, and challenges differ significantly. Let’s explore the key aspects of nursing careers in India and the U.S.
Nursing Careers in India and the U.S.
| Aspect | India | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Education Path | GNM, B.Sc., M.Sc., and diplomas | ADN, BSN, and advanced degrees |
| Licensing | State Nursing Council Registration | NCLEX-RN certification |
| Salary | ₹2.5 – ₹8 lakhs per annum | $60,000 – $150,000 annually |
| Work Environment | Overcrowded, especially in public hospitals | Well-structured with advanced technology |
| Career Growth | Limited within India, global opportunities | Extensive within and beyond clinical roles |
| Demand | Growing, especially in rural healthcare | High demand due to an aging population |
Overview of Nursing in India
India’s healthcare sector has been growing rapidly, increasing the demand for skilled nurses. Nurses in India play a crucial role in hospitals, clinics, and community healthcare settings.
Pediatric nurse
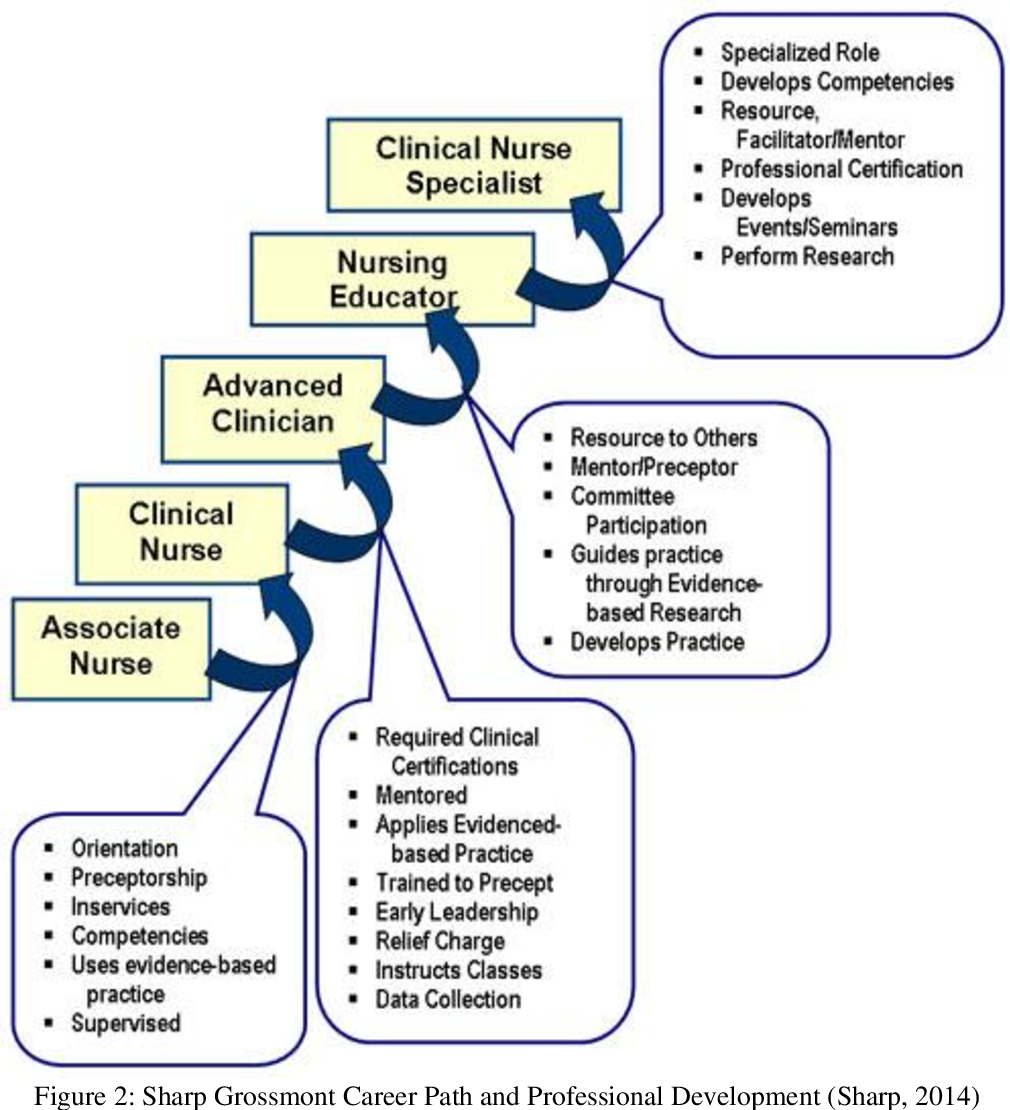
Key Features:
- Education: Diploma in General Nursing and Midwifery (GNM), Bachelor of Science in Nursing (B.Sc. Nursing), and Master’s programs.
- Work Settings: Government hospitals, private hospitals, and community health centers.
- Salary Range:
- Entry-level: ₹2.5 to ₹5 lakhs per annum.
- Experienced professionals: Up to ₹8 lakhs per annum or more.
- Challenges:
- High patient-to-nurse ratio.
- Limited access to advanced technologies in rural areas.
- Growth Opportunities:
- Nurses can specialize in fields like critical care, oncology, and pediatrics.
- Opportunities to work abroad, especially in Gulf countries and Western nations.
Overview of Nursing in the United States
The United States is renowned for its advanced healthcare system, offering excellent opportunities for nurses. Nursing is among the most respected and financially rewarding careers in the U.S.
Key Features:
- Education: Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), and advanced degrees like Nurse Practitioner (NP) programs.
- Work Settings: Hospitals, private practices, research institutions, and home healthcare.
- Salary Range:
- Entry-level: $60,000 to $80,000 annually.
- Experienced professionals: $90,000 to $150,000 or more annually.
- Challenges:
- High work pressure and demanding shifts.
- Requirement to pass the NCLEX-RN exam for licensure.
- Growth Opportunities:
- Specializations in areas like anesthetics, geriatrics, and informatics.
- Leadership roles and opportunities to influence healthcare policies.
Prospects for Indian Nurses in the U.S.
Indian nurses aspiring to work in the U.S. must fulfill certain requirements:
- Pass the NCLEX-RN exam.
- Obtain a visa and necessary certifications.
- Have fluency in English, often proven through exams like TOEFL or IELTS.
Once in the U.S., Indian nurses can benefit from higher salaries, better working conditions, and access to advanced medical technologies.
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary difference in nursing education between India and the U.S.? A: Nursing education in India focuses on diplomas and undergraduate degrees like GNM and B.Sc. Nursing. In the U.S., the emphasis is on ADN and BSN, with additional advanced degree opportunities.
Q2: Are Indian nursing degrees recognized in the U.S.? A: Indian nursing degrees are recognized, but candidates must pass the NCLEX-RN and meet state-specific licensing requirements.
Q3: Which country offers better financial prospects for nurses? A: The United States offers significantly higher salaries compared to India, but the cost of living is also higher.
Q4: Can Indian nurses specialize in the U.S.? A: Yes, Indian nurses can specialize in various fields after completing the necessary certifications.
Q5: Is there a demand for nurses in both countries? A: Yes, both India and the U.S. have a growing demand for skilled nurses due to expanding healthcare needs.
Table of Contents